In the ever-evolving world of finance, active investment management has emerged as a powerful tool for investors seeking to capitalize on market opportunities. This approach involves actively selecting and managing a portfolio of stocks, aiming to outperform the market through skillful stock picking and strategic allocation. This article delves into the intricacies of active investment management and its impact on U.S. stocks.
Understanding Active Investment Management
Active investment management is a method where fund managers actively seek to outperform the market by selecting individual stocks that they believe will outperform their peers. These managers employ a variety of strategies, including fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and qualitative assessment, to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks.
Key Strategies in Active Investment Management
Fundamental Analysis: This involves analyzing a company's financial statements, industry position, and management quality to determine its intrinsic value. Managers using this approach look for stocks that are undervalued relative to their fundamentals.
Technical Analysis: This method involves analyzing historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that could indicate future price movements. Technical analysts believe that market movements are predictable and can be used to inform investment decisions.
Quantitative Analysis: This approach uses mathematical models and algorithms to identify investment opportunities. Quantitative analysts rely on data and statistical analysis to make informed decisions.
Active Investment Management and U.S. Stocks
Active investment management has a significant impact on U.S. stocks. By actively managing their portfolios, fund managers can potentially capitalize on market inefficiencies and outperform the market. Here are some key points to consider:
Outperformance: Active managers often aim to outperform the market by selecting stocks that are undervalued or have the potential for significant growth. This can lead to higher returns for investors.
Risk Management: Active managers can adjust their portfolios to mitigate risk. For example, they may reduce exposure to sectors or companies that are facing significant challenges.
Market Timing: Active managers can take advantage of market fluctuations by buying low and selling high. This can lead to higher returns, especially in volatile markets.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of active investment management, let's consider a few case studies:
Fidelity Magellan Fund: This fund, managed by Peter Lynch from 1977 to 1990, achieved an average annual return of 29.2%. Lynch's active management style, which involved thorough research and a focus on undervalued stocks, played a significant role in the fund's success.
BlackRock's Active Equity Strategies: BlackRock, one of the world's largest asset managers, offers a range of active equity strategies. These strategies aim to outperform the market by selecting high-quality stocks and managing risk effectively.
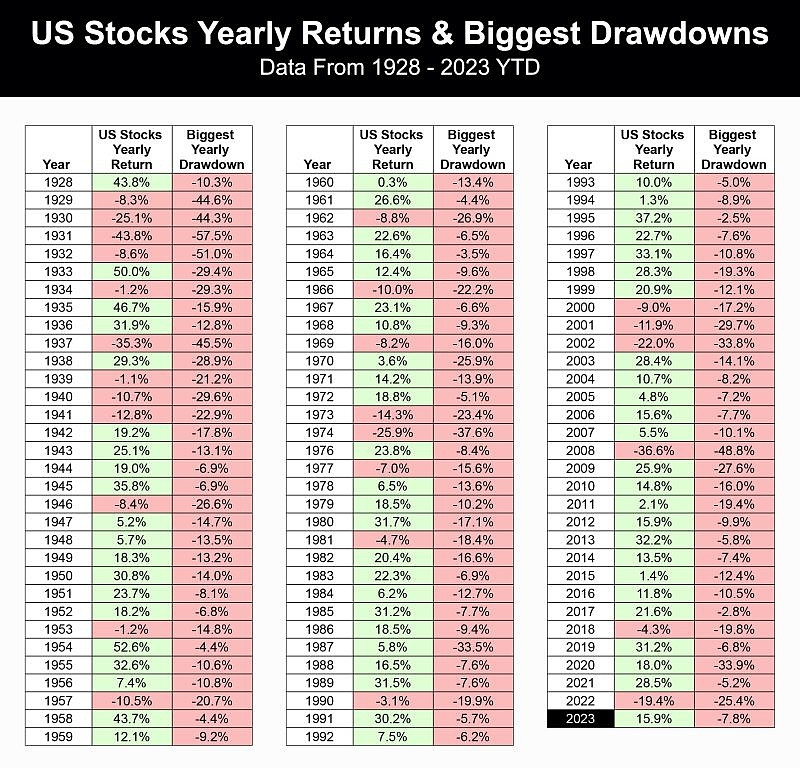
In conclusion, active investment management approaches U.S. stocks by employing various strategies to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks and outperform the market. While this approach comes with its own set of risks, the potential for higher returns makes it an attractive option for many investors.
nasdaq 100 companies