In the world of finance, the United States stock and bond markets are two of the most crucial components. They serve as the backbone of the global financial system, offering investors a variety of opportunities and risks. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the dynamics of these markets is essential. In this article, we will delve into the basics of US stocks and bonds, their differences, and how they can impact your investment strategy.
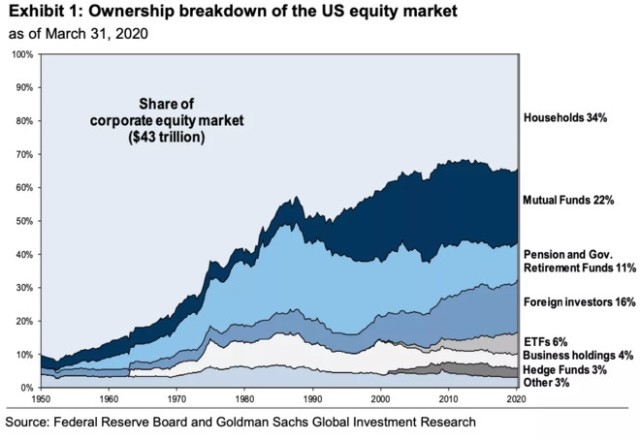
What are US Stocks?
US stocks represent ownership in a company. When you purchase a stock, you are essentially buying a small piece of that company. Stocks are considered high-risk, high-reward investments. While they offer the potential for significant returns, they can also experience significant volatility. Investors often buy stocks for the long term, hoping that the company will grow and increase in value over time.
Understanding Stock Market Indices
The stock market is often measured by various indices, such as the S&P 500, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the NASDAQ Composite. These indices track the performance of a basket of stocks and are used to gauge the overall health of the market. For example, the S&P 500 includes 500 large companies from various sectors, providing a comprehensive view of the stock market.
What are US Bonds?
US bonds, on the other hand, are debt securities issued by the U.S. government, municipalities, or corporations. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity. Bonds are considered lower-risk than stocks, as they offer fixed interest payments and the return of the principal.
Types of US Bonds
There are several types of US bonds, including:
The Relationship Between Stocks and Bonds
Investors often use a mix of stocks and bonds in their portfolios to balance risk and return. This strategy is known as asset allocation. By diversifying between stocks and bonds, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their portfolios.
Case Study: The 2008 Financial Crisis
One notable example of the relationship between stocks and bonds is the 2008 financial crisis. During this period, the stock market experienced a significant downturn, while bond prices remained relatively stable. Investors who held a diversified portfolio that included both stocks and bonds were better positioned to weather the storm.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of US stocks and bonds is crucial for any investor. By diversifying your portfolio and understanding the risks and rewards associated with each investment, you can make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals. Whether you are investing for long-term growth or seeking stable income, a well-balanced approach to US stocks and bonds can help you navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
nasdaq composite